Oracle E-Business Suite 12 Financials is a solution that provides
out-of-the-box features to meet global financial reporting and tax
requirements with one accounting, tax, banking, and payments model, and
makes it easy to operate shared services across businesses and regions.
we will start with recipes for creating Items.
We will cover:
-- Creating Items
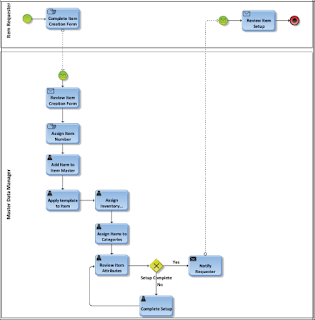
The following diagram details the process for creating Items:
1. The Item Requester (the person who requests an Item) completes an Item Creation Form, which should contain information such as:\
An Item template defines the Item Type. For example, a Finished Good template will identify certain characteristics that define the Item as a finished good, with attributes such as "Inventory Item" and "Stockable" with a value of "Yes". Let's look at how to create an Item in Oracle Inventory. We will also assign a Finished Good template to the Item.

Navigate to Items | Master Items. Please note that Items are defined in the Master Organization.
 Select Copy From from the tools menu (or press Alt+T). We are going to copy the attributes from the Finished Good template:
Select Copy From from the tools menu (or press Alt+T). We are going to copy the attributes from the Finished Good template:


Save the assignment.

Save the assignment.
Search for the Finished Good Item by navigating to Items | Master Items:



In the Inventory tab, check that the following are enabled:

In the Costing tab, check that the following are enabled: we will start with recipes for creating Items.
We will cover:
-- Creating Items
- Exploring Item attributes
- Creating Item templates
- Exploring Item controls
Introduction
An organization's operations include the buying and selling of products and services. Items can represent the products and services that are purchased and sold in an organization. Let's start by looking at the Item creation process.The following diagram details the process for creating Items:
1. The Item Requester (the person who requests an Item) completes an Item Creation Form, which should contain information such as:\
- Costing information
- Pricing Information
- Item and Product Categories
- Details of some of the Item attributes
- The inventory organization details
- Once complete, a message is sent to the Master Data Manager (the person who maintains the master data) to create the Item. The message could be sent by fax, e-mail, and so on.
- The Master Data Manager reviews the form and enters the details of the Item into Oracle E-Business Suite by creating the Item. Once complete, a message is sent to the Item Requester.
- The Item Requester reviews the Item setup on the system.
Creating Items
Oracle Inventory provides us with the functionality to create Items. Sets of attributes are assigned to an Item. The attributes define the characteristics of the Item. A group of attributes values defines a template, and a template can be assigned to an Item to automatically define the set of attribute values.An Item template defines the Item Type. For example, a Finished Good template will identify certain characteristics that define the Item as a finished good, with attributes such as "Inventory Item" and "Stockable" with a value of "Yes". Let's look at how to create an Item in Oracle Inventory. We will also assign a Finished Good template to the Item.
Getting ready
Log in to Oracle E-Business Suite R12 with the username and password assigned to you by the System Administrator. If you are working on the Vision demonstration database, you can use OPERATIONS/WELCOME as the USERNAME/PASSWORD:- Select the Inventory Responsibility.
- Select the V1 Inventory Organization.
How to do it...
Let's list the steps required to create an Item:Navigate to Items | Master Items. Please note that Items are defined in the Master Organization.
- Enter the Item code, for example, PRD20001.
- Enter a description for the Item:
- We can also copy attributes from an existing Item.
- Enter Finished Good and click on the Apply button (or press Alt+A) and click on the Done button.
- Save the Item definition by clicking on the Save icon (or press Ctrl+S).
How it works...
Items contain attributes and attributes contain information about an Item. Attributes can be controlled centrally at the Master Organization level or at the Inventory Organization level.There's more...
Once the Item is created, we need to assign it to a category and an inventory organization.Assigning Items to inventory organizations
For us to be able to perform transactions with the Item in the inventory, we need to assign the Item to an inventory organization. We can also use the organization Item form to change the attributes at the organization level. For example, an Item may be classified as raw materials in one organization and finished goods in another organization.- From the Tools menu, select Organization Assignment.
- Select the inventory organization for the Item. For example, A1–ACME Corporation. Click on the Assigned checkbox.
Save the assignment.
Assigning Items to categories
When an Item is created, it is assigned to a default category. However, you may want to perform transactions with the Item in more than one functional area, such as Inventory, Purchasing, Cost Management, Service, Engineering, and so on. You need to assign the Item to the relevant functional area. A category within a functional area is a logical classification of Items with similar characteristics.- From the Tools menu, select Categories.
- Select the Categories Set, Control Level, and the Category combination to assign to the Item:
Save the assignment.
Exploring Item attributes
There are more than 250 Item attributes grouped into 17 main attribute groups. In this recipe, we will explore the main groups that are used within the financial modules.How to do it...
Let's explore some Item attributes:Search for the Finished Good Item by navigating to Items | Master Items:
- Click on the Find icon. You then enter the Item code and click on the Find button to search for the Item.
- Select the tabs to review each of the attributes group:
- In the Main tab, check that the Item Status is Active. We can also enter a long description in the Long Description field.
- The default value of the primary Unit of Measure (UOM) can be defined in the INV: Default Primary Unit of Measure profile option. The value can be overwritten when creating the Item. The Primary UOM is the default UOM used in other modules. For example, in Receivables it is used for invoices and credit memos.
In the Inventory tab, check that the following are enabled:
- Inventory Item: It enables the Item to be transacted in Inventory. The default Inventory Item category is automatically assigned to the Item, if enabled.
- Stockable: It enables the Item to be stocked in Inventory.
- Transactable: Order Management uses this flag to determine how returns are transacted in Inventory.
- Reservable: It enables the reservation of Items during transactions. For example, during order entry in Order Management.
Costing: Enables the accounting for Item costs. It can be overridden in the Cost Management module, if average costing is used.
Cost of Goods Sold Account: The cost of goods sold account is entered. This is a general ledger account. The value defaults from the Organization parameters.
- In the Purchasing tab, enter a Default Buyer for the purchase orders, a List Price, and an Expense Account. Check that the following are enabled:
- Purchased: It enables us to purchase and receive the Item.
- Purchasable: It enables us to create a Purchase Order for the Item.
- Allow Description Update: It enables us to change the description of the Item when raising the Purchase Order.
- RFQ Required: Set this value to Yes to enable us to require a quotation for this Item.
- Taxable: Set this value to Yes with the Input Tax Classification Code as VAT–15%. This can be used with the default rules in E-Tax.
- Invoice Matching: Receipt Required–Yes. This is to allow for three-way matching.
- In the Receiving tab, review the controls.
In the Order Management tab, check that the following are enabled:
- Customer Ordered: This enables us to define prices for an Item assigned to a price list.
- Customer Orders Enabled: This enables us to sell the Item.
- Shippable: This enables us to ship the Item to the Customer.
- Internal Ordered: This enables us to order an Item via internal requisitions.
- Internal Orders Enabled: This enables us to temporarily exclude an Item from internal requisitions.
- OE Transactable: This is used for demand management of an Item.
In the Invoicing tab, enter values for the Accounting Rule, Invoicing Rule, Output Tax Classification Code, and Payment Terms. Enter the Sales Account code and check that the Invoiceable Item and Invoice Enabled checkboxes are enabled.